If you have Docker installed, opening up a Jupyter Python notebook with Pandas for data analysis can be done with one step on the command line. Running python notebooks in a Docker container prevents tons of headaches with installation, permissions, version conflicts, etc.
Docker Command
docker run --name notebookContainer --rm -p 127.0.0.1:8888:8888 -v pwd:/home/jovyan/work jeremyworks/jupyter-scipy:1.0.0
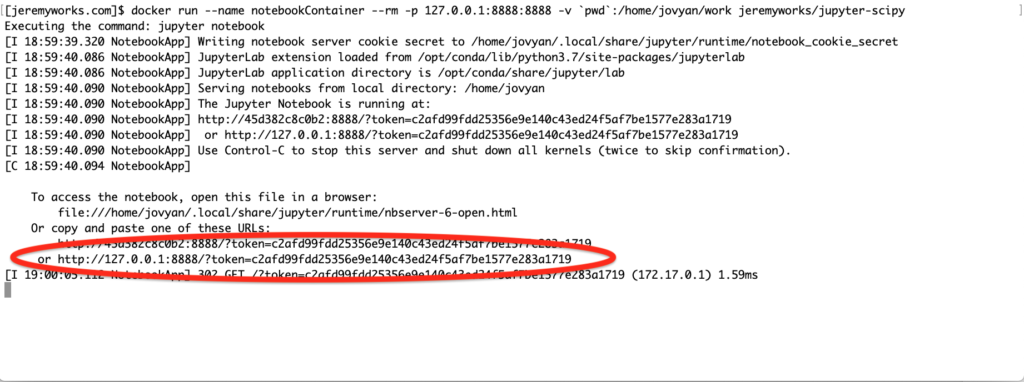
Docker Command Explained
- docker run – create and start a new container
- –name notebookContainer – name the new container to make it easier to identify
- –rm – remove the container when the docker run command finishes
- -p 127.0.0.1: 8888:8888 – map port 8888 of the container to port 8888 of localhost(127.0.0.1)
- -v `pwd`:/home/jovyan/work – map the current working directory to the notebook working directory. By mapping this volume to the same directory you can save and retrieve notebooks created during previous Docker run commands
- jeremyworks/jupyter-scipydocker – docker image to run. When the version tag is left out this is the same as specifying jeremyworks/jupyter-scipydocker:latest
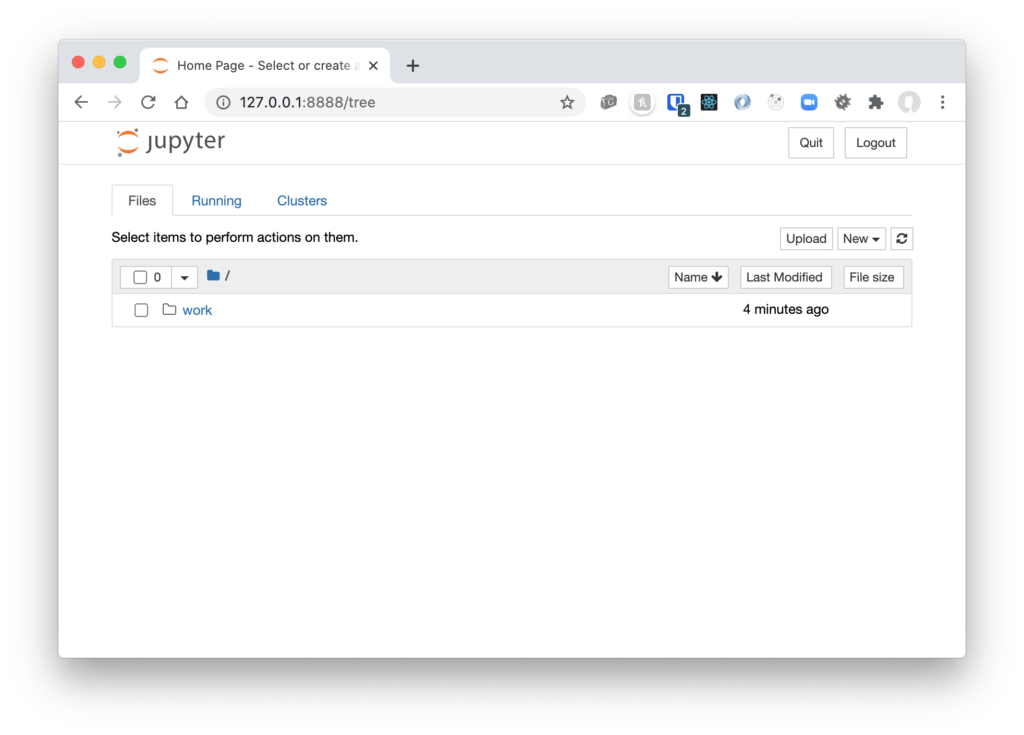
Browser Access
Paste the URL copied from the console output starting with, http://127.0.0.1:8888/ , into a browser.
This URL includes a token for access to the new Jupyter server running in Docker.
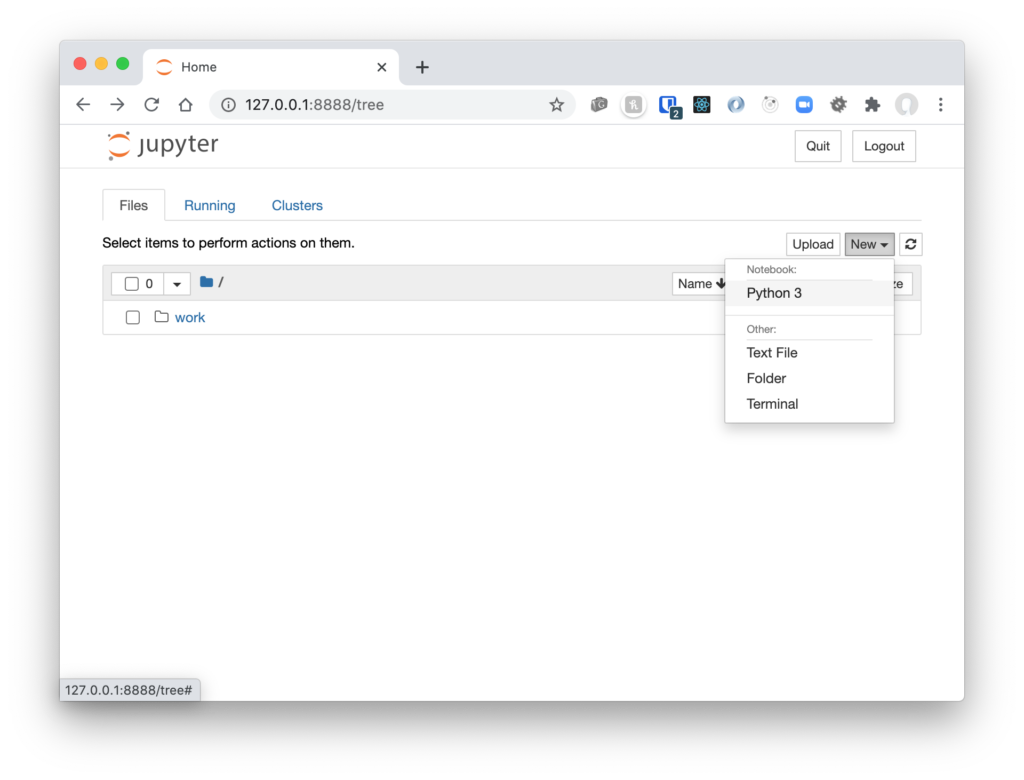
Create a New Notebook
Select New/ Python 3
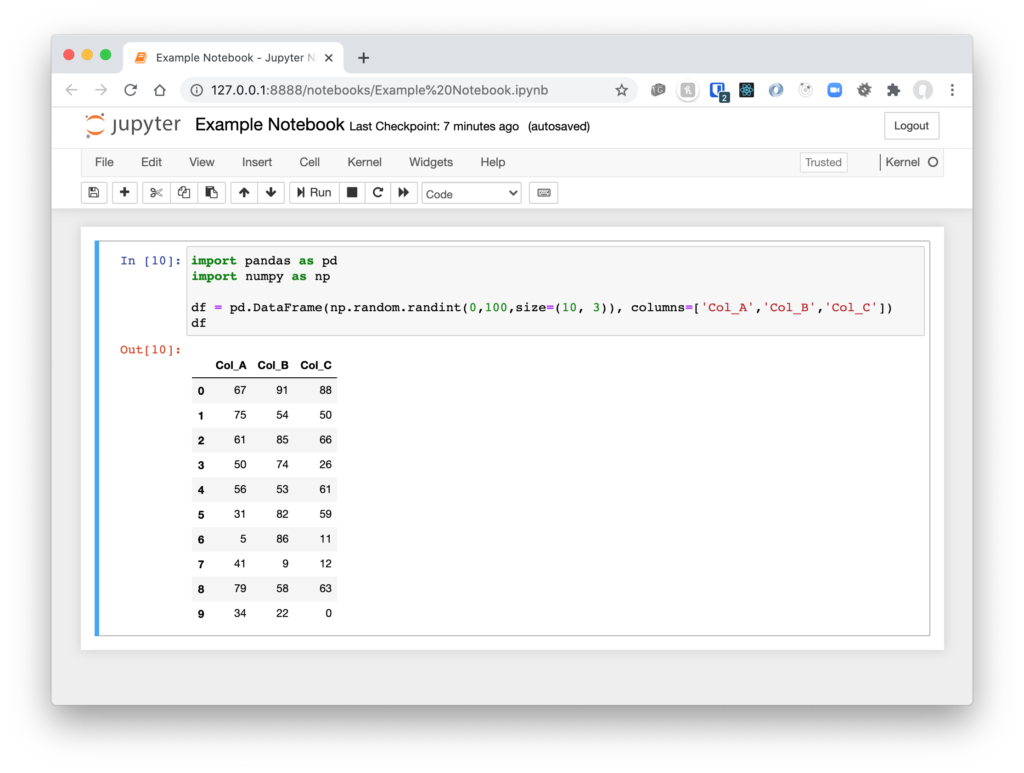
Try it out
Here’s some example code to create a DataFrame
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0,100,size=(10, 3)), columns=['Col_A','Col_B','Col_C']) df
Links
- Jeremyworks Docker Repo- https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/jeremyworks/jupyter-scipy
- Jupyter Notebooks- https://jupyter.org/
- Pandas- https://pandas.pydata.org/
- Docker Run Command – https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/run/
- Pandas Dataframe- https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.html